A Combination Of 2'fucosyllactose And Osteopontin Attenuates 2,4 - Dinitrochlorobenzene (Dncb)- Induced Contact Dermatitis Murine Model
- Topical Area: Nutrition/Neonatal and preterm nutrition
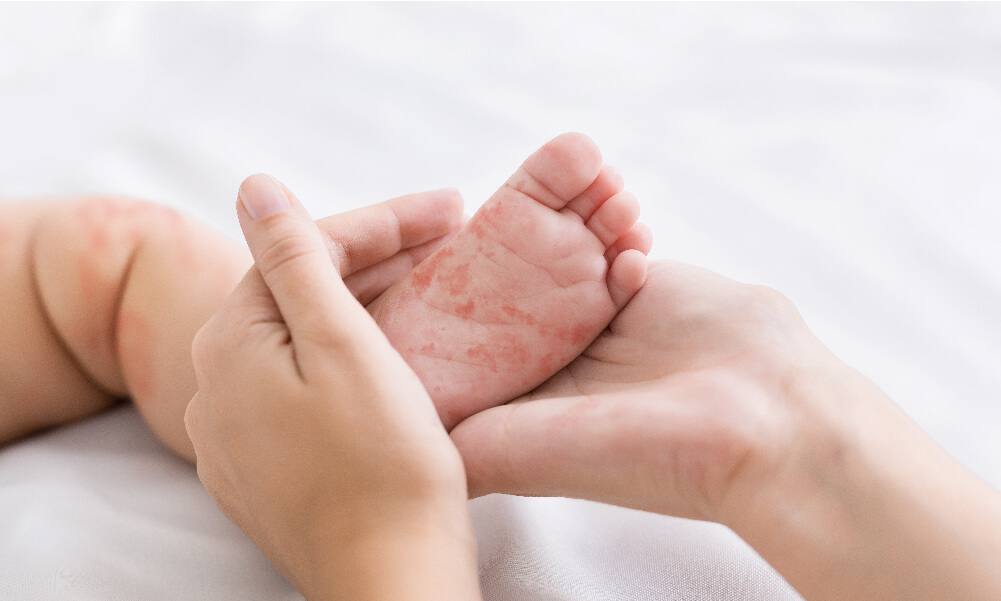
Topic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease that is often associated with skin barrier dysfunction leading to a higher frequency of bacterial and viral skin infections. The protective effect of breastfeeding against the development of AD and other allergic diseases is well accepted but not fully understood. In this study, the impact of osteopontin (OPN), a multi-functional glycoprotein found in mothers’ milk, and 2´-fucosyllactose (2′-FL), the predominant human milk oligosaccharide, alone or in combination, was determined on AD-like symptoms.
Repeated epicutaneous application of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) was performed on the ear and dorsal skin of BALB/c mice to induce AD-like symptoms and skin lesions. Oral administrations of OPN and/or 2′-FL at concentrations commonly associated with mature mothers’ milk were performed and AD-like symptoms, behavior, water loss, immune cell activation, immunoglobulin and cytokine expression was recorded.
OPN and/or 2′-FL decreased serum IgE levels and limited the infiltration of eosinophils and mast cells to the dermal tissues in the DNCB-induced AD mice. Furthermore, OPN and 2′-FL reduced Th2 and Th17 responses, leading to an attenuated cutaneous inflammatory response. Interestingly, combinations of OPN and 2-FL had a more pronounced effect on IgE expression, eosinophil and Th cell response when compared to the use of OPN or 2-FL alone.
It could be concluded that OPN and 2′-FL synergistically attenuate DNCB-induced AD-like skin lesion in a murine model through modulating T cell-elicited immune responses and CD4+ T cell polarization.
Southern Medical University, Department of Immunology School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, China, 2H&H Group, Global Research and Technology Center, Cork, Ireland, H&H Group, Global Research and Technology Center, Guangzhou, China
Are you a Healthcare Professional?
Important Notice and Declaration
Breast milk is best for babies. Professional advice should be followed before using an infant formula. Introducing partial bottle feeding could negatively affect breast feeding. Good maternal nutrition is important for breast feeding and reversing a decision not to breast feed may be difficult. Infant formula should always be used as directed. Proper use of an infant formula is important to the health of the infant. Social and financial implications should be considered when selecting a method of feeding.
The information provided on this website is intended for use by healthcare professionals only. It is a condition of use of this site that you are a healthcare professional within the meaning of regulations within your country of practice. Then denoting below Yes I am/No icons. For Healthcare Professionals based in Australia : It is a condition of use of this site that you are a healthcare professional within the meaning of the Marketing in Australia of Infant Formulas (MAIF) Agreement or the Therapeutic Goods Act.